
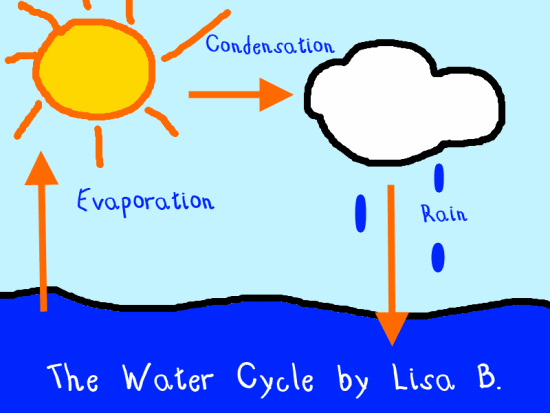
Snowpacks in warmer climates often thaw and melt when spring arrives, and the melted water flows overland as snowmelt. Some precipitation falls as snow and can accumulate as ice caps and glaciers, which can store frozen water for thousands of years. The vapor rises into the air where cooler temperatures cause it to condense into clouds.Īir currents move clouds around the globe, cloud particles collide, grow, and fall out of the sky as precipitation.

Rising air currents take the vapor up into the atmosphere, along with water from evapotranspiration, which is water transpired from plants and evaporated from the soil. Ice and snow can sublimate directly into water vapor. Some of it evaporates as vapor into the air. The sun, which drives the water cycle, heats water in the oceans. But, we'll begin in the oceans, since that is where most of Earth's water exists. Volcanic activity kept and still keeps introducing water in the atmosphere, thus increasing the surface- and groundwater volume of the Earth.
#Clipart collection water cycle free#
Water set free by magma began to cool down the Earth's atmosphere, until it could stay on the surface as a liquid. Where does all the Earth's water come from? Primordial Earth was an incandescent globe made of magma, but all magmas contain water. Access in-depth information about each component of the water cycle:Ī (very) quick summary of the water cycle


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
